Tools
MApp-KG
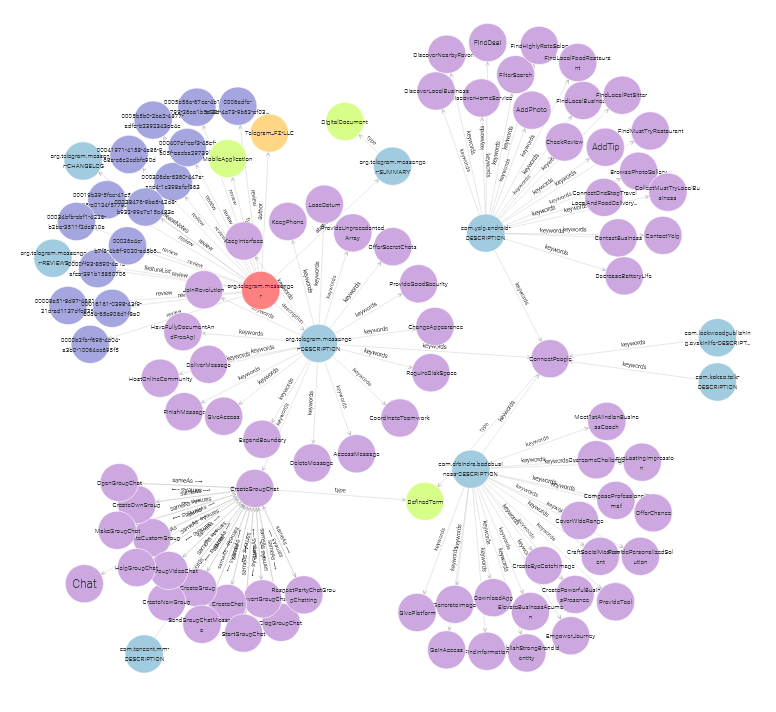
Name: MApp-KG: Mobile App Knowledge Graph for Document-based Feature Knowledge Generation
Description: A combination of software resources and data artefacts in the field of mobile app repositories aimed at supporting feature-oriented knowledge generation tasks.
Authors: Quim Motger, Xavier Franch, Jordi Marco
RE-Miner
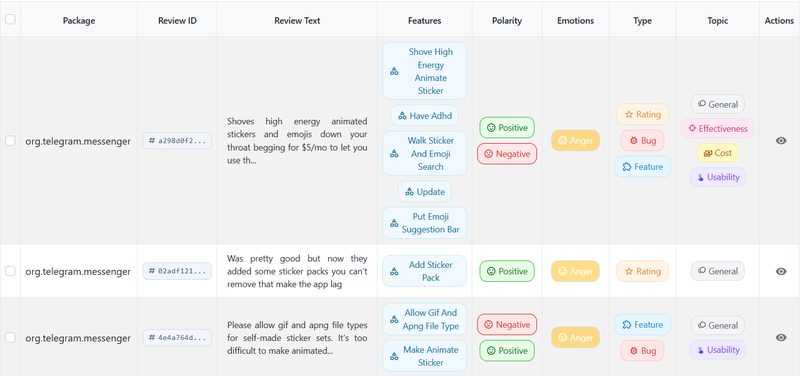
Name: RE-Miner 2.0: A Holistic Framework for Mining Mobile Application Reviews
Description: A web application tool that integrates multiple data extraction and analysis methods in a distributed environment, enabling a multidimensional and detailed analysis of user feedback from app stores, such as features, emotions, review types and topics.
Authors: Max Tiessler, Quim Motger
NLP4SE Feature Extraction
Name: Mobile App Feature Extraction from User Reviews
Description: A combination of software-based and model-based contributions to extract mobile app features from user-generated reviews..
Authors: Quim Motger, Xavier Franch, Jordi Marco, Agustí Gállego
Learning Dashboard Suite
Description: The Learning Dashboard Suite includes several interconnected tools to track, analyze, and enhance teamwork in educational and industrial software engineering projects.
It integrates data from development tools and computes and visualizes learning and performance metrics.
MLAssetSelection
Name: MLAssetSelection
Description: This web application can be used to choose your open-source ML asset for software engineering tasks. With the tool assets as pre-trained models and datasets can be found.
Authors: Alexandra González, Oscar Cerezo, Xavier Franch, Silverio Martínez-Fernández
MLSToolbox

Description: MLSToolbox aims to provide a set of tools to support the development of Machine Learning Systems (MLS).
Tools: MLS Code Generator, MLS Code Assessment
Team: Claudia Ayala, Cristina Gómez, Lidia López
Links of interest:
- Access to the MLSToobox in the following link
- The source code is publicly available at GitHub
- Documentation is available at GitHub Wiki
- Some videos for MLS Code Generator are available at a dedicated page on the GitHub Wiki
You can contact us in the following email address: mlstoolbox-request@mylist.upc.edu
SOPCOM
Name: SOPCOM
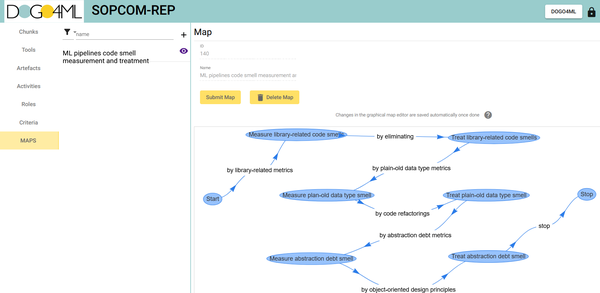
Description: Situational Method Engineering (SME) principles and techniques have been proposed to promote the modularization of method knowledge in the form of reusable method components and their composition into new situation specific methods. SOPCOM is a tool aimed at supporting the creation and management of an SME method components (“chunks”) catalogue, and the composition of these components into methods.
Authors:
- Project coordinators: Dolors Costal, Carme Quer
- Implementation: Carlos Plana, Marc Duch, Fèlix Forroll
Share: